Cocaine addiction is a serious and complex problem that affects millions of people worldwide. One of the biggest challenges for those struggling with cocaine abuse is dealing with powerful and persistent cravings. These cravings can be incredibly intense and often lead to relapse if not managed effectively. What are some strategies for coping with cocaine cravings and breaking the cycle of addiction?
The Cycle of Addiction
People who struggle with substance abuse typically follow a three-part loop known as the cycle of addiction.1 It goes as follows:
- Binge/Intoxication: The person experiences the rewarding effects and feelings of a drug or alcohol binge, including euphoria, reduced anxiety, and eased social interactions.
- Negative Affect/Withdrawal: The person experiences withdrawal effects that come after a substance binge and the negative feelings of a “crash”
- Preoccupation/Anticipation: Once the negative effects wear off, the person begins experiencing the excitement and anticipation of the next binge
People follow this cycle of addiction over and over until they choose to seek help or someone intervenes and encourages them to go to treatment.
Understanding Cocaine Addiction
Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant drug that affects the brain’s reward system. Regular use of cocaine can lead to changes in the brain that make it difficult to control cravings and impulses.2 Cocaine cravings can be triggered by various cues, including environmental triggers, emotional stress, or social situations. Understanding these triggers is the first step in learning to cope with and overcome cocaine cravings.
Breaking the Cocaine Addiction Cycle
If you’re ready to break the cocaine addiction cycle, the following steps will make for a good start:
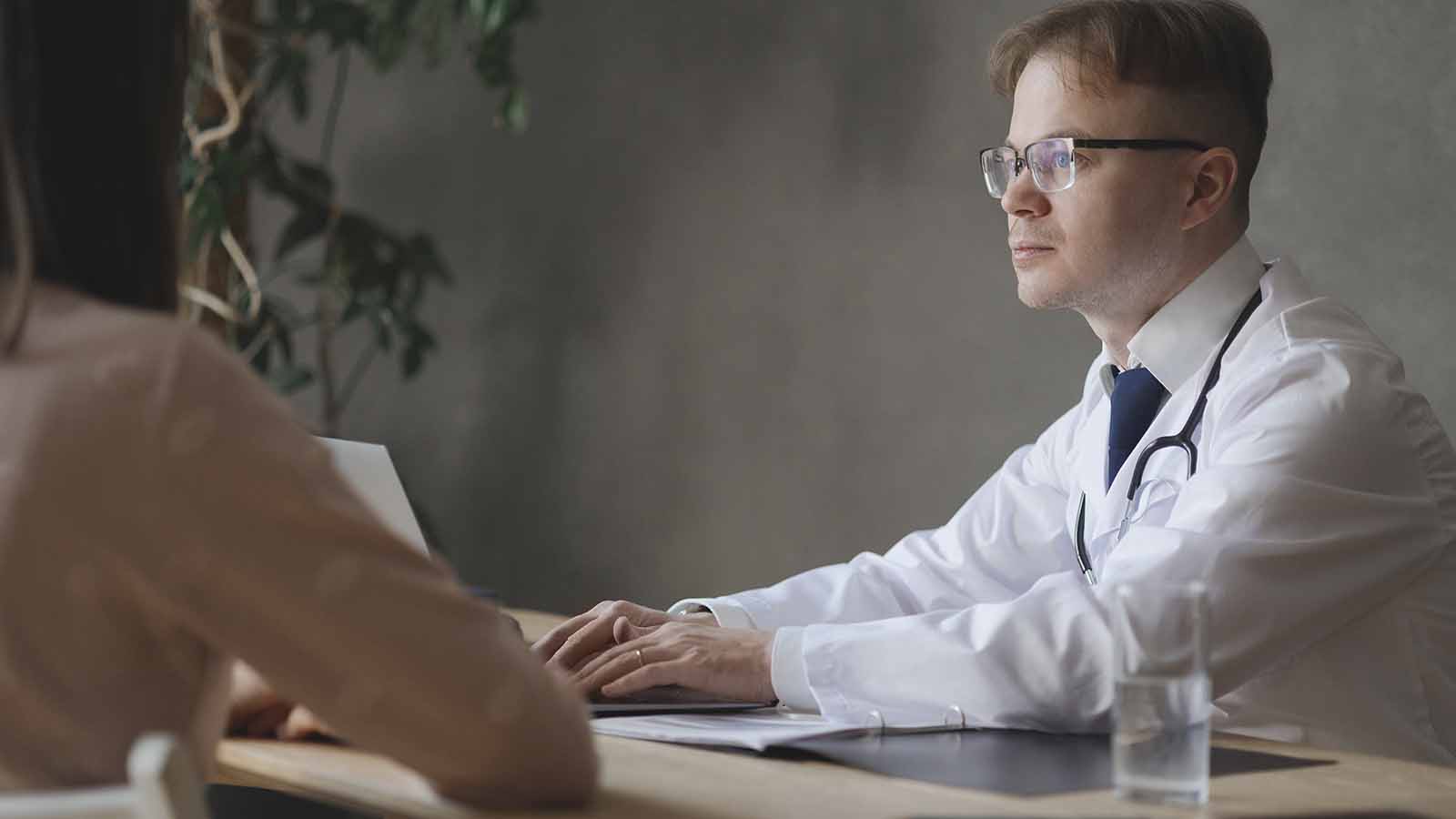
Seek Professional Help
Coping with cocaine cravings often requires professional guidance and support. Consider seeking help from a specialized addiction treatment program. There you’ll receive an individualized treatment plan that may include therapy, medication, or a combination of the two.
Identify and Avoid Triggers
Recognizing and avoiding triggers that lead to cocaine cravings is crucial. These triggers vary from person to person, but common ones include stress, social situations, specific people, and places associated with drug use. Once you recognize your triggers, you can develop strategies to avoid or cope with them.
Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Finding healthy ways to cope with stress and difficult emotions is essential in overcoming cocaine cravings. Engaging in activities like exercise, meditation, and mindfulness can help you manage stress and reduce the urge to use cocaine.
Create a Supportive Environment
Building a supportive environment is key to breaking the cycle of cocaine addiction. Share your goals with family and friends, and let them know how they can support you. Surround yourself with a supportive network of people who understand your struggle and are willing to help.
Develop a Relapse Prevention Plan
A relapse prevention plan is a personalized strategy to help you stay on track during recovery. It involves identifying potential triggers, creating strategies to deal with cravings, and keeping a support system in place to call upon when needed. Your plan should be flexible and adaptable, as recovery is an ongoing process.
Stay Mindful and Present
Practicing mindfulness can be a powerful tool in managing cocaine cravings. Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, can help you stay present in the moment and prevent your mind from dwelling on past drug use or future cravings.
Coping with cocaine cravings is a challenging process, but it’s essential for breaking the cycle of addiction. Seeking professional help from an addiction treatment program like Steps to Recovery is one of the best things you can do. Find a location near you today and reach out when you’re ready to end the cycle of addiction and take your life back.
References
- National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism. (2021). The Cycle of Alcohol Addiction.
- Science & Practice Perspectives. (2005). The Neurobiology of Cocaine Addiction.
Explore this article:
Explore Our Facilities
Drug and alcohol detox and residential treatment for addiction and mental health disorders
Outpatient treatment center for substance use disorder and mental health disorders
Outpatient treatment center for substance use disorder and co-occurring mental health disorders